PKP2-hiPSC
UKJi001-A
General
Cell Line |
|
| hPSCreg name | UKJi001-A |
| Cite as: | UKJi001-A (RRID:CVCL_E7UQ) |
| Alternative name(s) |
PKP2-hiPSC
|
| Cell line type | Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) |
| Similar lines |
|
| Last update | 14th June 2024 |
| Notes | The absence of early markers and treatment options for arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is a major indication of our inadequate understanding of the disease. Furthermore, it is still unknown how metabolic dysregulation relates to ARVC disease. Patients with ARVC often have genetic mutations in the genes encoding cardiac desmosome proteins, most commonly in PKP2, the gene that codes for plakophilin-2. The precise pathways that result in the manifestations of ARVC illness are unknown. Physical exercise is one of the most important factors that promotes the phenotypic expression and the progression of the disease. |
| User feedback | |
Provider |
|
| Generator | Universitätsklinikum Jena (UKJ), Klinik für Innere Medizin I (KIM I), Dr. M. Bekhite ELsaied (UKJ) |
| Owner | Universitätsklinikum Jena (UKJ), Klinik für Innere Medizin I (KIM I), Dr. M. Bekhite ELsaied (UKJ) |
| Distributors | |
| Derivation country | Germany |
External Databases |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA115717852 |
| Cellosaurus | CVCL_E7UQ |
General Information |
|
| Publications | |
| * Is the cell line readily obtainable for third parties? |
Yes Research use: allowed
Clinical use: not allowed
Commercial use: not allowed
Additional restrictions:
Permitted the PKP2-hiPSC to be used exclusively for research purposes following the signing of a collaboration agreement. |
Donor Information
General Donor Information |
|
| Sex | male |
| Age of donor (at collection) | 30-34 |
| Ethnicity | Age: 32 year-old, Ethnicity: Caucasian |
Phenotype and Disease related information (Donor) |
|
| Diseases | No disease was diagnosed.
|
| Disease associated phenotypes | no phenotypes |
| Family history | The father (61-year-old), harboring the same PKP2 heterozygous mutation with a clinical diagnosis of ARVC disease phenotype. |
| Is the medical history available upon request? | No |
| Is clinical information available? | No |
Karyotyping (Donor) |
|
| Has the donor karyotype been analysed? |
Unknown
|
Other Genotyping (Donor) |
|
| Is there genome-wide genotyping or functional data available? |
Yes
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)
heterozygous PKP2 mutations in Exon 1, c.184C>T |
Donor Relations |
|
| All cell lines of this donor's relatives |
Has father:
|
External Databases (Donor) |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA115717853 |
Ethics
| Has informed consent been obtained from the donor of the embryo/tissue from which the pluripotent stem cells have been derived? | Yes |
| Was the consent voluntarily given? | Yes |
| Has the donor been informed that participation will not directly influence their personal treatment? | Yes |
| Can you provide us with a copy of the Donor Information Sheet provided to the donor? | Yes |
| Do you (Depositor/Provider) hold the original Donor Consent Form? | Yes |
| Confirm that consent was obtained by a qualified professional | Yes |
| Has the donor agreed to be re-contacted? | Yes |
| Has the donor been informed about how her/his data will be protected? | Yes |
| Please indicate whether the data associated with the donated material has been pseudonymised or anonymised. | pseudonymised |
| Does consent explicitly allow the derivation of pluripotent stem cells? | Yes |
| * Does consent expressly prevent the derivation of pluripotent stem cells? | No |
| * Does consent pertain to a specific research project? | Yes |
| Details on restriction to research project | Creation of patient-specific iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs) |
| Does consent permit unforeseen future research, without further consent? | No |
| Does the consent permit uses of donated embryo/tissue or derived cell line intended for clinical treatment or human applications? | No |
| Does consent expressly prevent development of commercial products? | Yes |
| Does consent expressly prevent financial gain from any use of the donated embryo/tissue, including any product made from it? | Yes |
| Does consent expressly permit storage of donated embryo/tissue for an unlimited time? | Yes |
| Does consent expressly permit storage of cells derived from the donated embryo/tissue for an unlimited time? | Yes |
| Does consent prevent the DONATED BIOSAMPLE from being made available to researchers anywhere in the world? | No |
| Does consent prevent CELLS DERIVED FROM THE DONATED BIOSAMPLE from being made available to researchers anywhere in the world? | No |
Does consent permit research by | |
| an academic institution? | Yes |
| a public organisation? | No |
| a for-profit corporation? | No |
| Does consent expressly permit collection of genetic information? | Yes |
| Does consent expressly permit storage of genetic information? | Yes |
| Does consent prevent dissemination of genetic information? | Yes |
| Has the donor been informed that their donated biosample or derived cells may be tested for the presence of microbiological agents / pathogens? | Yes |
| Has the donor consented to receive information discovered during use of donated embryo/tissue that has significant health implications for the donor? | No |
| How may genetic information associated with the cell line be accessed? | Controlled Access |
| Will the donor expect to receive financial benefit, beyond reasonable expenses, in return for donating the biosample? | No |
| Does the consent anticipate that the donor will be notified of results or outcomes of any research involving the donated samples or derived cells? | No |
| Does the consent permit the donor, upon withdrawal of consent, to stop the use of the derived cell line(s) that have already been created from donated samples? | Yes |
| Does the consent permit the donor, upon withdrawal of consent, to stop delivery or use of information and data about the donor? | Yes |
| Has a favourable opinion been obtained from a research ethics committee, or other ethics review panel, in relation to the Research Protocol including the consent provisions? | Yes |
| Name of accrediting authority involved? | University of Jena Ethics Committee |
| Approval number | 2020-1833/1-Material and 2022-2853/1-Material |
| Has a favourable opinion been obtained from a research ethics committee, or other ethics review panel, in relation to the PROPOSED PROJECT, involving use of donated embryo/tissue or derived cells? | No |
| Do you have obligations to third parties in regard to the use of the cell line? | No |
| Are you aware of any further constraints on the use of the donated embryo/tissue or derived cells? | No |
| Is there an MTA available for the cell line? | No |
| For generation of the cell line, who was the supplier of any recombined DNA vectors or commercial kits used? | Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific |
| Are you aware of any constraints on the use or distribution of the cell line from the owner or any parties identified in the query above? | No |
hIPSC Derivation
General |
|
| Source cell line name | Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell |
| Source cell type |
A peripheral blood cell with a single nucleus. This category includes lymphocytes and monocytes.
Synonyms
|
| Source cell origin |
A liquid tissue; its major function is to transport oxygen throughout the body. It also supplies the tissues with nutrients, removes waste products, and contains various components of the immune system defending the body against infection. Several hormones also travel in the blood.
Synonyms
|
| Age of donor (at collection) | 30-34 |
| Collected in | 2021 |
| Source cell line vendor | Klinik für Innere Medizin I, Universitätsklinikum Jena |
| Passage number reprogrammed | 0 |
Reprogramming method |
|
| Vector type | Non-integrating |
| Vector | Sendai virus |
| Genes | |
| Is reprogramming vector detectable? |
No |
| Methods used |
PCR
|
| Notes on reprogramming vector detection | Confirmation of the absence of the Sendai-Virus in iPSC-WT cell line |
| Files and images showing reprogramming vector expressed or silenced | |
Vector free reprogramming |
|
| Type of used vector free reprogramming factor(s) |
None
|
Other |
|
| Selection criteria for clones | IPSC clones were manually picked and cultured on Matrigel (Corning) coated plate using mTeSR1 (Stem Cell) at 37 °C, 5% CO 2. We pick a single colony from passage 1 and subcloning for 10 passages and then testing for virus free iPSC. |
| Derived under xeno-free conditions |
Yes |
| Derived under GMP? |
No |
| Available as clinical grade? |
No |
Culture Conditions
| Surface coating | Matrigel/Geltrex |
| Feeder cells |
No |
| Passage method |
Enzyme-free cell dissociation
ReLeSR™ is an enzyme-free reagent for dissociation and passaging of human embryonic stem (ES) or induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells
|
| O2 Concentration | 20 % |
| CO2 Concentration | 5 % |
| Medium | mTeSR™ 1 |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at passage previously with this cell line? | Yes |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at cryo previously with this cell line? | No |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at thaw previously with this cell line? | Yes |
Characterisation
Analysis of Undifferentiated Cells
| Marker | Expressed | Immunostaining | RT-PCR | Flow Cytometry | Enzymatic Assay | Expression Profiles |
| POU5F1 (OCT-4) |
Yes |
|||||
| TRA 1-60 |
Yes |
|||||
| SOX2 |
Yes |
|||||
| SSEA-4 |
Yes |
Score:
| Marker | Present | Absent |
| mCpG | ||
| OCT4 |
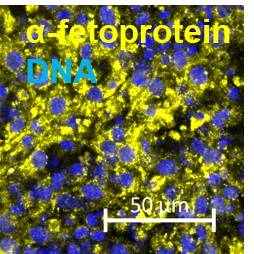
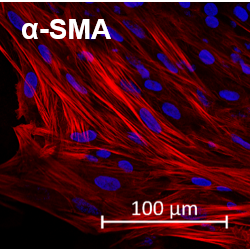
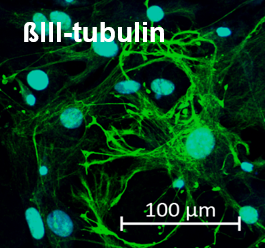
Pluripotency was verified by staining the colony with alkaline phosphatase and examining how the cells differentiated into three germ layers by forming ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm structures in sections of embryoid bodies stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Method documentation
Alkaline phosphatase PKP2-iPSC.png
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining
Microbiology / Virus Screening |
|
| HIV 1 | Negative |
| Hepatitis B | Negative |
| Hepatitis C | Negative |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
Genotyping
Karyotyping (Cell Line) |
|
| Has the cell line karyotype been analysed? |
Yes
Karyotyping shows the genomic integrity in iPSC after reprogramming
Passage number: 15
Karyotyping method:
G-Banding
|
Other Genotyping (Cell Line) |
|
| Is there genome-wide genotyping or functional data available? |
Yes
Sanger sequencing analysis
heterozygous PKP2 mutations in Exon 1, c.184C>T |



Login to share your feedback, experiences or results with the research community.