DKH005i-A, DKHi005-A
KSCBi010-A
General
Cell Line |
|
| hPSCreg name | KSCBi010-A |
| Cite as: | KSCBi010-A (RRID:CVCL_WR22) |
| Alternative name(s) |
DKH005i-A, DKHi005-A
|
| Cell line type | Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) |
| Similar lines |
IMBAi021-A (TSC107J #5, TSC#14 clone 107J#5) Donor's gene variants: TSC2, TSC2 Donor diseases: Tuberous Sclerosis IMBAi022-A (TSC112#4, TSC#24 clone 112#4) Donor's gene variants: TSC2, TSC2 Donor diseases: Tuberous Sclerosis IMBAi023-A (TSC#5 clone 32S, TSCp5#32S) Donor's gene variants: TSC2, TSC2 Donor diseases: Tuberous Sclerosis IMBAi023-B (TSC#5 clone 30S, TSCp5#30S, TSC98#30S) Donor's gene variants: TSC2, TSC2, TSC2 Donor diseases: Tuberous Sclerosis PFIZi023-A (B217c8) Donor's gene variants: GPR56, GPR56 Donor diseases: Bilateral Frontoparietal Polymicrogyria ZJSHi001-A (ZJSHi-KCNB1) Donor's gene variants: KCNB1 Donor diseases: developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, 26 |
| Last update | 9th January 2024 |
| User feedback | |
Provider |
|
| Generator | National Stem Cell Bank (KSCB) |
| Owner | National Stem Cell Bank (KSCB) |
| Distributors | |
| Derivation country | South Korea |
External Databases |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA5892403 |
| Cellosaurus | CVCL_WR22 |
| Wikidata | Q95980264 |
General Information |
|
| Publications | |
| * Is the cell line readily obtainable for third parties? |
Yes Research use: allowed
Clinical use: not allowed
Commercial use: not allowed
|
Donor Information
General Donor Information |
|
| Sex | female |
Phenotype and Disease related information (Donor) |
|
| Diseases | A disease was diagnosed.
|
External Databases (Donor) |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA5892404 |
Ethics
| Has informed consent been obtained from the donor of the embryo/tissue from which the pluripotent stem cells have been derived? | Yes |
| Was the consent voluntarily given? | Yes |
| Has the donor been informed that participation will not directly influence their personal treatment? | Yes |
| Can you provide us with a copy of the Donor Information Sheet provided to the donor? | No |
| Do you (Depositor/Provider) hold the original Donor Consent Form? | No |
| If you do not hold the Donor Consent Form, do you know who does? | Yes |
| Please indicate whether the data associated with the donated material has been pseudonymised or anonymised. | anonymised |
| Does consent explicitly allow the derivation of pluripotent stem cells? | Yes |
| Does consent prevent CELLS DERIVED FROM THE DONATED BIOSAMPLE from being made available to researchers anywhere in the world? | Yes |
| How may genetic information associated with the cell line be accessed? | Open Access |
| Will the donor expect to receive financial benefit, beyond reasonable expenses, in return for donating the biosample? | No |
| Has a favourable opinion been obtained from a research ethics committee, or other ethics review panel, in relation to the Research Protocol including the consent provisions? | Yes |
| Name of accrediting authority involved? | Yonsei university health system, severance hospital, institutional review board |
| Approval number | 4-2016-1158 |
| Has a favourable opinion been obtained from a research ethics committee, or other ethics review panel, in relation to the PROPOSED PROJECT, involving use of donated embryo/tissue or derived cells? | Yes |
| Name of accrediting authority involved? | Yonsei university health system, severance hospital, institutional review board |
| Approval number | 4-2016-1158 |
| For generation of the cell line, who was the supplier of any recombined DNA vectors or commercial kits used? |
hIPSC Derivation
General |
|
| Source cell type |
A peripheral blood cell with a single nucleus. This category includes lymphocytes and monocytes.
Synonyms
|
| Source cell origin |
A liquid tissue; its major function is to transport oxygen throughout the body. It also supplies the tissues with nutrients, removes waste products, and contains various components of the immune system defending the body against infection. Several hormones also travel in the blood.
Synonyms
|
Reprogramming method |
|
| Vector type | Non-integrating |
| Vector | Sendai virus |
| Genes | |
| Is reprogramming vector detectable? |
No |
| Methods used |
PCR
|
| Files and images showing reprogramming vector expressed or silenced | |
Vector free reprogramming |
|
Other |
|
| Derived under xeno-free conditions |
Unknown |
| Derived under GMP? |
Unknown |
| Available as clinical grade? |
Unknown |
Culture Conditions
| Surface coating | Vitronectin |
| Feeder cells |
No |
| Passage method |
Enzyme-free cell dissociation
EDTA
|
| Medium |
TeSR™ E8™
|
Characterisation
Analysis of Undifferentiated Cells
| Marker | Expressed | Immunostaining | RT-PCR | Flow Cytometry | Enzymatic Assay | Expression Profiles |
| POU5F1 (OCT-4) |
Yes |
|||||
| SSEA-4 |
Yes |
|
||||
| TRA 1-60 |
Yes |
|
||||
| TRA 1-81 |
Yes |
|
||||
| NANOG |
Yes |
|
||||
| SOX2 |
Yes |
|
||||
| ZFP42 (REX-1) |
Yes |
|
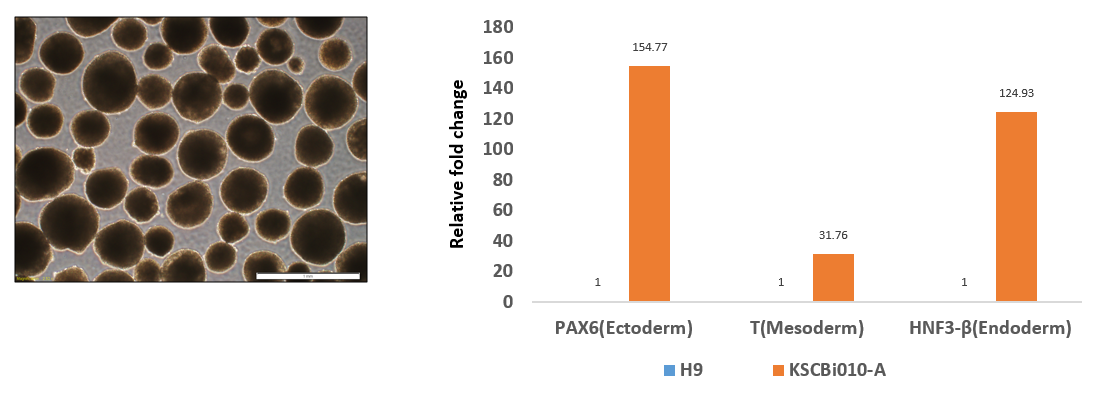
Differentiation Potency
In vitro spontaneous differentiation
| Marker | Expressed |
| FOXA2 |
Yes |
Genotyping
Karyotyping (Cell Line) |
|
| Has the cell line karyotype been analysed? |
Yes
|
Other Genotyping (Cell Line) |
|


Login to share your feedback, experiences or results with the research community.