PH-BL-414 Clone 16, iLB-296bfs16
The cell line is not validated yet.
LBi016-B
General
Cell Line |
|
| hPSCreg name | LBi016-B |
| Cite as: | LBi016-B (RRID:CVCL_C6RC) |
| Alternative name(s) |
PH-BL-414 Clone 16, iLB-296bfs16
|
| Cell line type | Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) |
| Similar lines |
LBi016-A (PH-BL-414 Clone 10, iLB-296bfs10) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi017-A (PH-BL-401 Clone 22, iLB-280bfs22) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi017-B (PH-BL-401 Clone 36, iLB-280bfs36) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi018-A (PH-BL-409 Clone 43, iLB-291bfs43) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi018-B (PH-BL-409 Clone 45, iLB-291bfs45) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi019-A (PH-BL-901 Clone 154, iLB-275bms154) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi019-B (iLB-275bms162, PH-BL-901 Clone 162) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi020-A (iLB-294bms22, PH-BL-412 Clone 238) Donor's gene variants: TREM2, TREM2 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi001-A (PH-BL-001 Clone 4, iLB-268bfs4) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi001-B (iLB-268bfs9, PH-BL-001 Clone 9) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi002-A (PH-BL-002 Clone 2, iLB-272bfs2) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi002-B (PH-BL-002 Clone 9, iLB-272bfs9) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi004-A (PH-BL-204 Clone 210, iLB-278bfs210) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi004-B (PH-BL-204 Clone 211, iLB-278bfs211) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi003-A (iLB-273bms57, PH-BL-003 Clone 57) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi003-B (PH-BL-003 Clone 61, iLB-273bms61) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi005-A (iLB-293bms257, PH-BL-411 Clone 257) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease LBi005-B (iLB-293bms258, PH-BL-411 Clone 258) Donor's gene variants: CD33, CD33, CD33, CD33 Donor diseases: Alzheimer disease |
| Last update | 1st March 2023 |
| User feedback | |
Provider |
|
| Generator | Life & Brain GmbH (LB) |
| Distributors | |
| Derivation country | Germany |
External Databases |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA111531214 |
| Cellosaurus | CVCL_C6RC |
| Wikidata | Q117704624 |
General Information |
|
| * Is the cell line readily obtainable for third parties? |
Yes Research use: allowed
Clinical use: allowed
Commercial use: not allowed
|
Donor Information
General Donor Information |
|
| Sex | female |
| Age of donor (at collection) | 60-64 |
| Ethnicity | White European |
Phenotype and Disease related information (Donor) |
|
| Diseases | A disease was diagnosed.
|
Karyotyping (Donor) |
|
| Has the donor karyotype been analysed? |
Unknown
|
Donor Relations |
|
| Other cell lines of this donor | |
External Databases (Donor) |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA111531222 |
Ethics
| Has informed consent been obtained from the donor of the embryo/tissue from which the pluripotent stem cells have been derived? | Yes |
| Was the consent voluntarily given? | Yes |
| Has the donor been informed that participation will not directly influence their personal treatment? | Yes |
| Can you provide us with a copy of the Donor Information Sheet provided to the donor? | Yes |
| Do you (Depositor/Provider) hold the original Donor Consent Form? | No |
| If you do not hold the Donor Consent Form, do you know who does? | Yes |
| Please indicate whether the data associated with the donated material has been pseudonymised or anonymised. | pseudonymised |
| Does consent explicitly allow the derivation of pluripotent stem cells? | Yes |
| * Does consent expressly prevent the derivation of pluripotent stem cells? | No |
| * Does consent pertain to a specific research project? | No |
| Does consent permit unforeseen future research, without further consent? | Yes |
| Does consent expressly prevent development of commercial products? | No |
| Does consent expressly prevent financial gain from any use of the donated embryo/tissue, including any product made from it? | No |
| Does consent prevent the DONATED BIOSAMPLE from being made available to researchers anywhere in the world? | No |
| Does consent prevent CELLS DERIVED FROM THE DONATED BIOSAMPLE from being made available to researchers anywhere in the world? | No |
| How may genetic information associated with the cell line be accessed? | Controlled Access |
| Will the donor expect to receive financial benefit, beyond reasonable expenses, in return for donating the biosample? | No |
| Does the consent permit the donor, upon withdrawal of consent, to stop the use of the derived cell line(s) that have already been created from donated samples? | No |
| Does the consent permit the donor, upon withdrawal of consent, to stop delivery or use of information and data about the donor? | Yes |
| Has a favourable opinion been obtained from a research ethics committee, or other ethics review panel, in relation to the Research Protocol including the consent provisions? | Yes |
| Name of accrediting authority involved? | Health Research Authority |
| Approval number | 224771 |
| Do you have obligations to third parties in regard to the use of the cell line? | Yes |
| Please describe: | EMDA and L&B |
| Are you aware of any further constraints on the use of the donated embryo/tissue or derived cells? | No |
| For generation of the cell line, who was the supplier of any recombined DNA vectors or commercial kits used? |
hIPSC Derivation
General |
|
| Source cell type |
Committed, erythroid stem cells derived from myeloid stem cells. The progenitor cells develop in two phases: erythroid burst-forming units (bfu-e) followed by erythroid colony-forming units (cfu-e). Bfu-e differentiate into cfu-e on stimulation by erythropoietin, and then further differentiate into erythroblasts when stimulated by other factors.
|
| Source cell origin |
A liquid tissue; its major function is to transport oxygen throughout the body. It also supplies the tissues with nutrients, removes waste products, and contains various components of the immune system defending the body against infection. Several hormones also travel in the blood.
Synonyms
|
| Age of donor (at collection) | 60-64 |
| Collected in | 2018 |
Reprogramming method |
|
| Vector type | Non-integrating |
| Vector | Sendai virus |
| Is reprogramming vector detectable? |
No |
| Methods used |
RT-PCR
|
| Files and images showing reprogramming vector expressed or silenced | |
Vector free reprogramming |
|
Other |
|
| Derived under xeno-free conditions |
No |
| Derived under GMP? |
No |
| Available as clinical grade? |
No |
Culture Conditions
| Surface coating | Vitronectin |
| Feeder cells |
No |
| Passage method |
Enzyme-free cell dissociation
EDTA
|
| O2 Concentration | 20 % |
| CO2 Concentration | 6 % |
| Medium |
Other medium:
Base medium: StemMACS™ iPS-Brew XF, Basal Medium
Main protein source: StemMACS™ iPS Brew XF, 50x Supplement Serum concentration: % |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at passage previously with this cell line? | Yes |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at cryo previously with this cell line? | No |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at thaw previously with this cell line? | Yes |
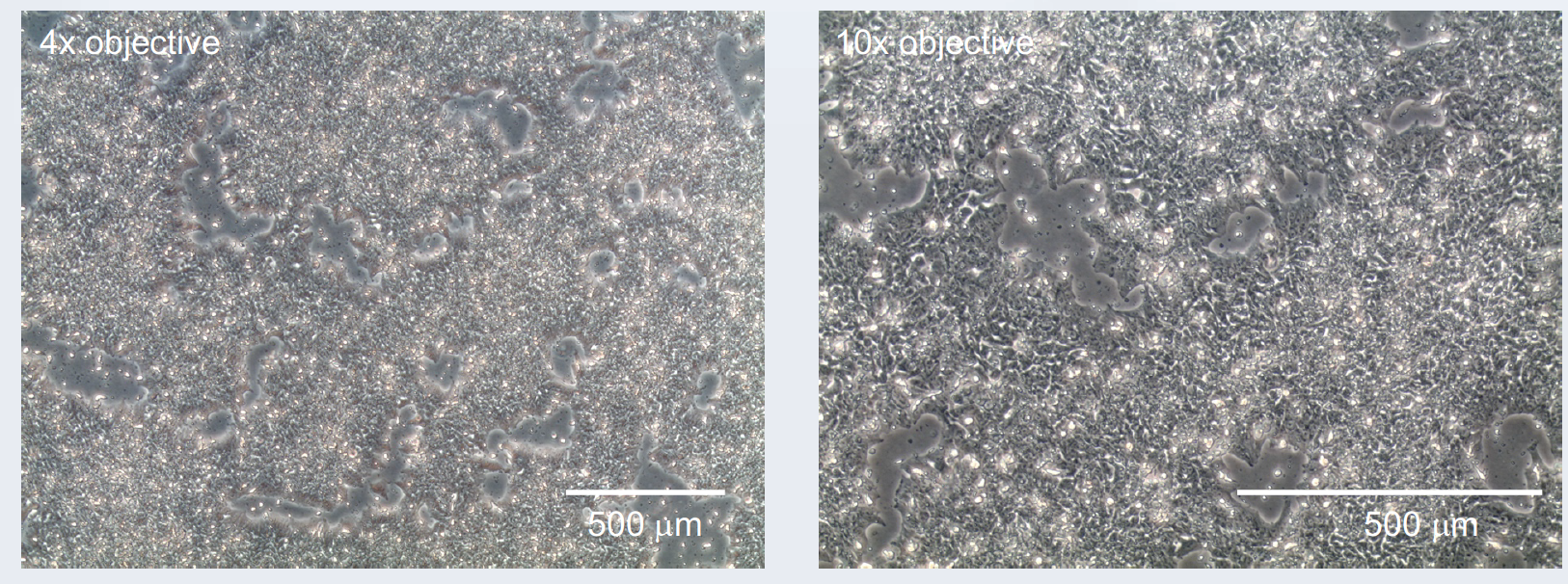
Characterisation
Genotyping
Karyotyping (Cell Line) |
|
| Has the cell line karyotype been analysed? |
Yes
46XX, 1 CNV > 1MB was found on chromosome 6 of both, patient and corresponding iPS cell line
|
Other Genotyping (Cell Line) |
|


Login to share your feedback, experiences or results with the research community.