iFCI004
CRICKi005-A
General
Cell Line |
|
| hPSCreg name | CRICKi005-A |
| Cite as: | CRICKi005-A (RRID:CVCL_C3R0) |
| Alternative name(s) |
iFCI004
|
| Cell line type | Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) |
| Similar lines |
SAPi004-A (ALS III, TDP43-A382T/A382T, ALS III-TDP43-A382T/A382T) Donor diseases: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis HIHDNDi001-A (A30P-3, SNCA3, Tue_020_A) Donor's gene variants: SNCA, SNCA, SNCA Donor diseases: autosomal dominant Parkinson disease 1 HIHDNDi001-B (A30P-4, SNCA4, Tue_020_B) Donor's gene variants: SNCA, SNCA, SNCA Donor diseases: autosomal dominant Parkinson disease 1 |
| Last update | 12th December 2022 |
| User feedback | |
Provider |
|
| Generator | The Francis Crick Institute Limited (CRICK) |
External Databases |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA112226452 |
| Cellosaurus | CVCL_C3R0 |
| Wikidata | Q116048788 |
General Information |
|
| Publications | |
| * Is the cell line readily obtainable for third parties? |
Yes Research use: allowed
Clinical use: not allowed
Commercial use: not allowed
|
Donor Information
General Donor Information |
|
| Sex | male |
Phenotype and Disease related information (Donor) |
|
| Diseases | A disease was diagnosed.
|
Karyotyping (Donor) |
|
| Has the donor karyotype been analysed? |
Yes
The KaryoStat™ assay allows for digital visualization of chromosome aberrations with a resolution similar to g-banding karyotyping by relying on 150k SNP probes across the human genome. The size of structural aberration that can be detected is > 2 Mb for chromosomal gains and > 1 Mb for chromosomal losses. The assay enables the detection of aneuploidies, submicroscopic aberrations, and mosaic events.
Karyotyping method:
G-Banding
|
Other Genotyping (Donor) |
|
| Is there genome-wide genotyping or functional data available? |
No
|
External Databases (Donor) |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA112224409 |
Ethics
| Has informed consent been obtained from the donor of the embryo/tissue from which the pluripotent stem cells have been derived? | Yes |
| Was the consent voluntarily given? | Yes |
| Has the donor been informed that participation will not directly influence their personal treatment? | Yes |
| Can you provide us with a copy of the Donor Information Sheet provided to the donor? | Yes |
| Do you (Depositor/Provider) hold the original Donor Consent Form? | No |
| If you do not hold the Donor Consent Form, do you know who does? | Yes |
| Alternatives to consent are available? | No |
| Is there other documentation provided to the donor for consenting purposes? | No |
| Confirm that consent was obtained by a qualified professional | Yes |
| Has the donor agreed to be re-contacted? | Unknown |
| Has the donor been informed about how her/his data will be protected? | Yes |
| Please indicate whether the data associated with the donated material has been pseudonymised or anonymised. | anonymised |
| Does consent explicitly allow the derivation of pluripotent stem cells? | Yes |
| * Does consent expressly prevent the derivation of pluripotent stem cells? | No |
| * Does consent pertain to a specific research project? | No |
| Does consent permit unforeseen future research, without further consent? | Yes |
| Does the consent permit uses of donated embryo/tissue or derived cell line intended for clinical treatment or human applications? | No |
| Does consent expressly permit storage of donated embryo/tissue for an unlimited time? | Yes |
| Does consent expressly permit storage of cells derived from the donated embryo/tissue for an unlimited time? | Yes |
| Does consent prevent the DONATED BIOSAMPLE from being made available to researchers anywhere in the world? | No |
| Does consent prevent CELLS DERIVED FROM THE DONATED BIOSAMPLE from being made available to researchers anywhere in the world? | Yes |
Does consent permit research by | |
| an academic institution? | Yes |
| a public organisation? | Yes |
| a non-profit company? | Yes |
| a for-profit corporation? | No |
| How may genetic information associated with the cell line be accessed? | No information |
| Will the donor expect to receive financial benefit, beyond reasonable expenses, in return for donating the biosample? | No |
| Has a favourable opinion been obtained from a research ethics committee, or other ethics review panel, in relation to the Research Protocol including the consent provisions? | Yes |
| Name of accrediting authority involved? | The London – West London & GTAC Research Ethics Committee (formerly known as the Hammersmith, Queen Charlotte's and Chelsea Research Ethics Committee). |
| Approval number | 08ND17 |
| For generation of the cell line, who was the supplier of any recombined DNA vectors or commercial kits used? | |
hIPSC Derivation
General |
|
| Source cell type |
Synonyms
|
Reprogramming method |
|
| Vector type | None |
Vector free reprogramming |
|
| Type of used vector free reprogramming factor(s) |
mRNA
|
| mRNA | |
Other |
|
| Selection criteria for clones | Manually picked by best morphology |
| Derived under xeno-free conditions |
No |
| Derived under GMP? |
No |
| Available as clinical grade? |
No |
Culture Conditions
| Surface coating | Matrigel/Geltrex |
| Feeder cells |
No |
| Passage method |
Enzyme-free cell dissociation
Gentle Cell Dissociation Reagent
|
| O2 Concentration | 5 % |
| CO2 Concentration | 5 % |
| Medium |
mTeSR™ 1
|
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at passage previously with this cell line? | No |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at cryo previously with this cell line? | No |
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at thaw previously with this cell line? | Yes |
Characterisation
Analysis of Undifferentiated Cells
| Marker | Expressed | Immunostaining | RT-PCR | Flow Cytometry | Enzymatic Assay | Expression Profiles |
| POU5F1 (OCT-4) |
Yes |
Method documentation
Flow Cytometry FIGURE iFCI004.png
FLOW CYTOMETRY
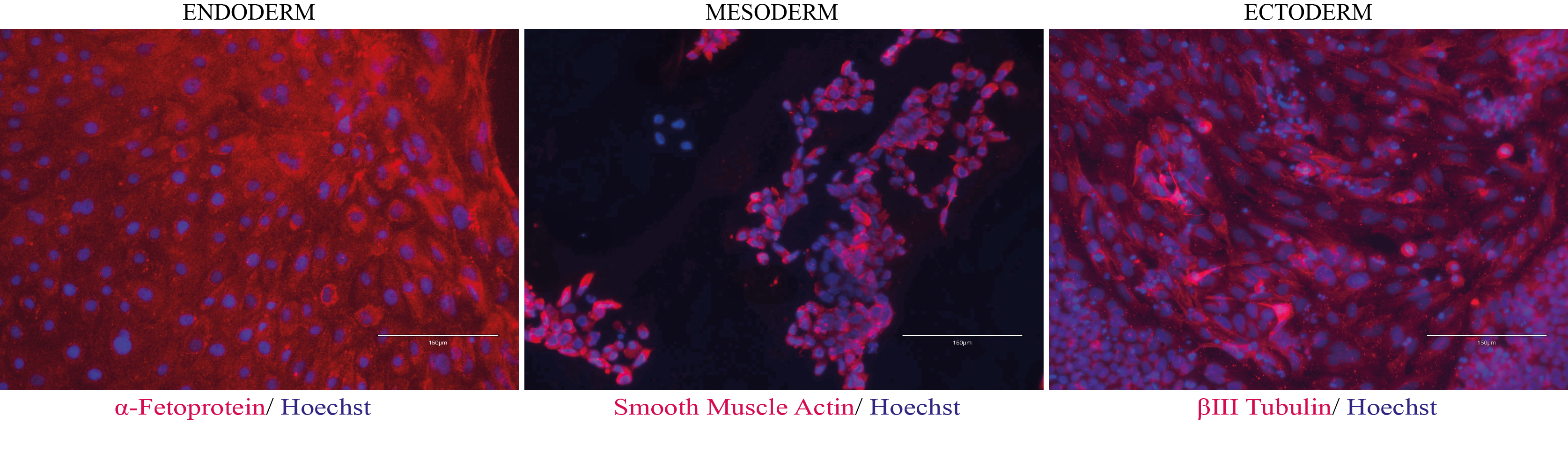
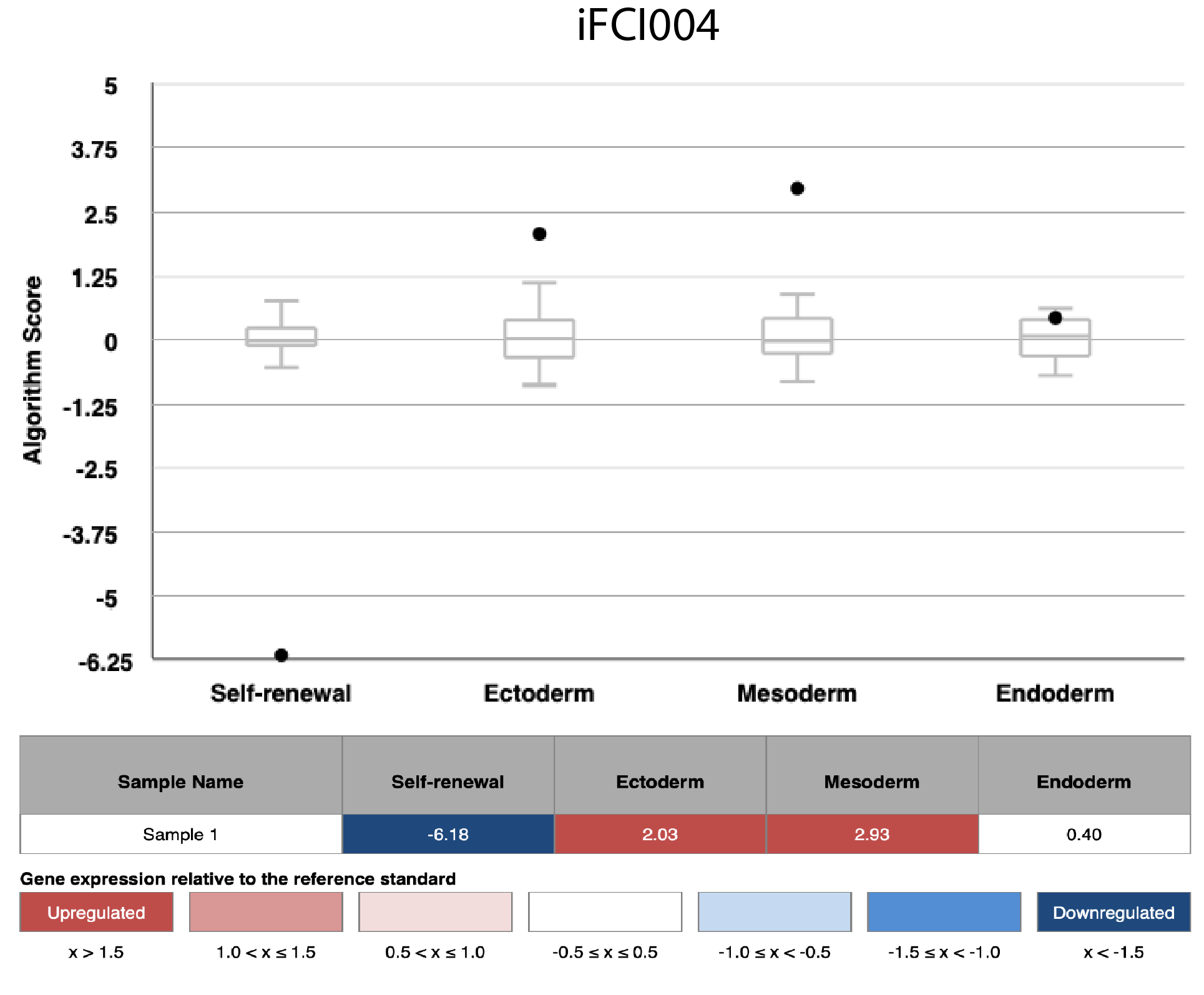
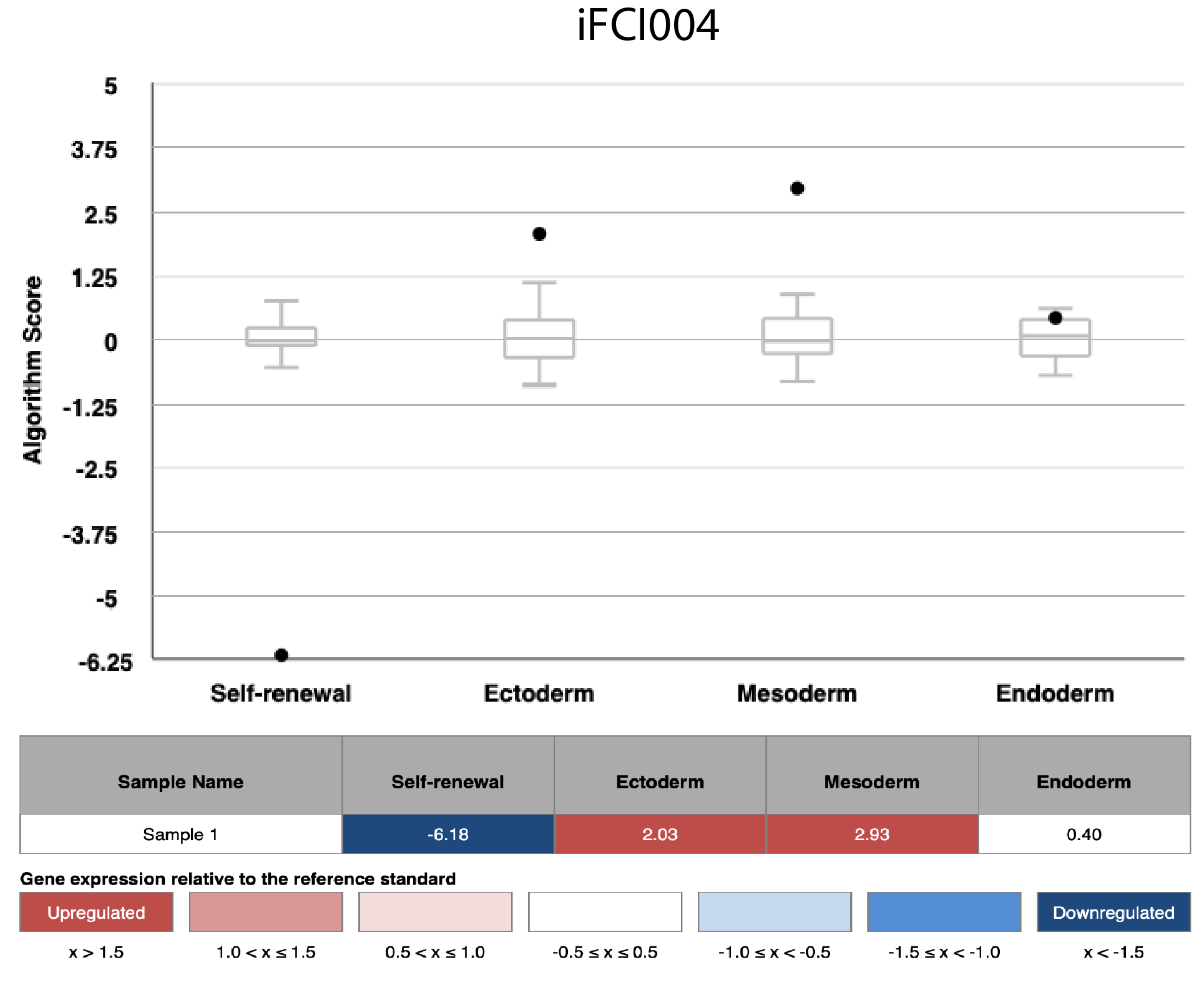
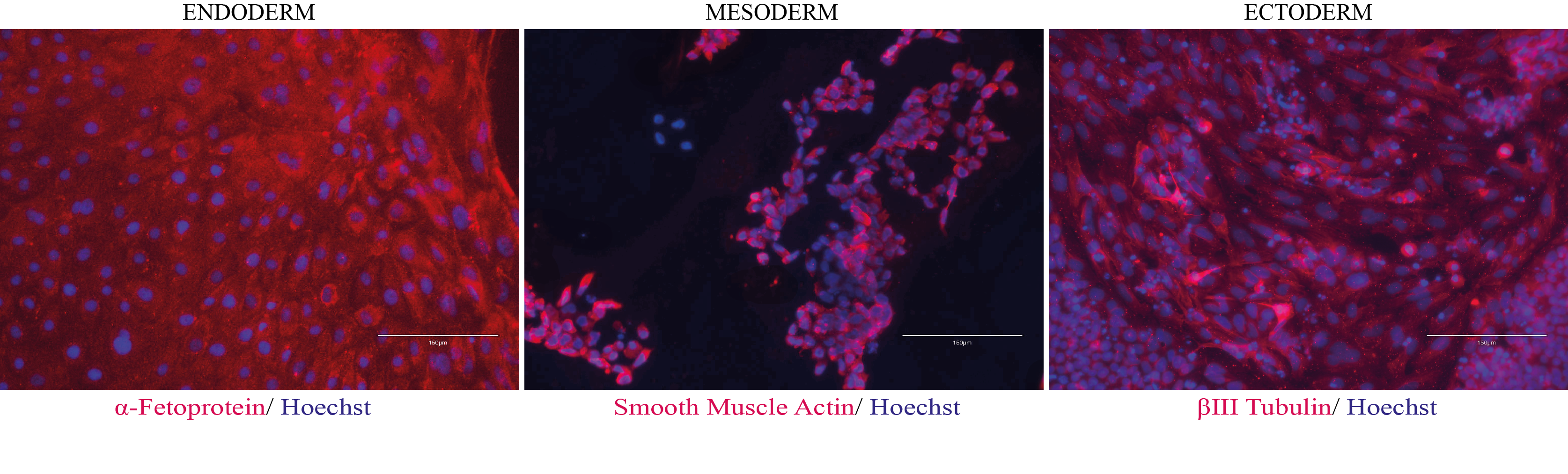
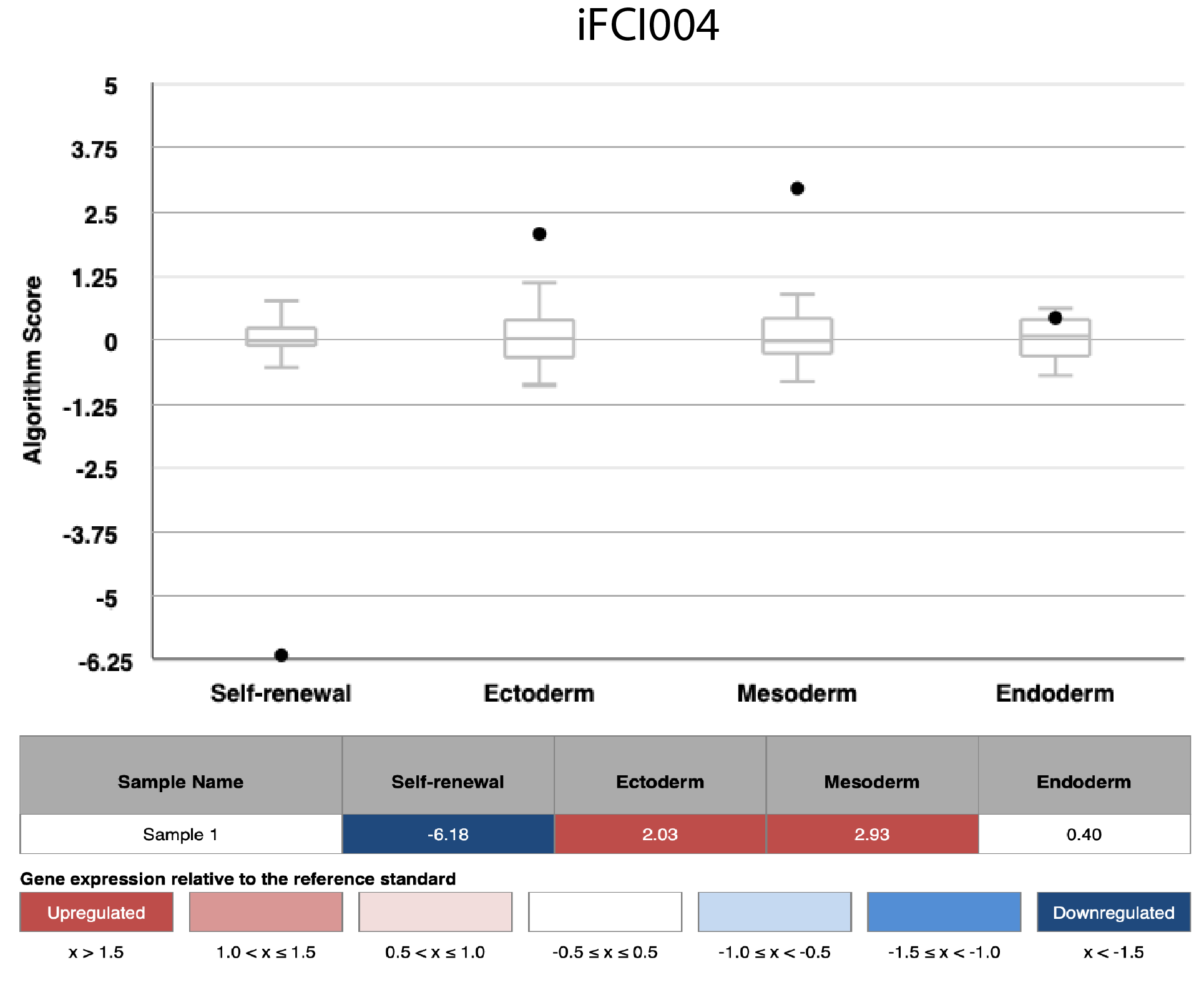
Differentiation Potency
In vitro spontaneous differentiation
In vitro directed differentiation
Scorecard
In vitro spontaneous differentiation
In vitro directed differentiation
Scorecard
In vitro spontaneous differentiation
In vitro directed differentiation
Scorecard
Microbiology / Virus Screening |
|
| HIV 1 | Negative |
| HIV 2 | Negative |
| Hepatitis B | Negative |
| Hepatitis C | Negative |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
Genotyping
Karyotyping (Cell Line) |
|
| Has the cell line karyotype been analysed? |
Yes
The KaryoStat™ assay allows for digital visualization of chromosome aberrations with a resolution similar to g-banding karyotyping by relying on 150k SNP probes across the human genome. The size of structural aberration that can be detected is > 2 Mb for chromosomal gains and > 1 Mb for chromosomal losses. The assay enables the detection of aneuploidies, submicroscopic aberrations, and mosaic events.
Karyotyping method:
G-Banding
|
Other Genotyping (Cell Line) |
|



Login to share your feedback, experiences or results with the research community.