K6-4fpCyto-16
ICGi021-A-2
General
Cell Line |
|
| hPSCreg name | ICGi021-A-2 |
| Cite as: | ICGi021-A-2 |
| Alternative name(s) |
K6-4fpCyto-16
|
| Cell line type | Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) |
| Similar lines |
ICGi021-A-1 (K6-4fpCyto-13) ICGi021-A-3 (K6-4fpCyto-19) ICGi021-A (K6-4f) MRIi001-A-1 (C6-AAVS1-iCasRx) WAe007-A-5 (H7-AP1-Luciferase-GFP) UCSFi001-A-36 (AICS-0036-028) UCSFi001-A-82 (WTC11-SLC12A3) UCSFi001-A-12 (AICS-0036-006) CRMi003-A-3 (Proliving, GMNN-mScarletI Reporter) MRIi003-A-7 (HK-AAVS1-iCasRx) MRIi003-A-8 (HK-AAVS1-CAG-eGFP-homo) UCSFi001-A-23 (AICS-0054-091) UCSFi001-A-1D (AICS-0120-204) UCSFi001-A-1E (AICS-0102-330) BIHi001-A-1 (iBCRT Cas9v1-3G-Kl.16) |
| Last update | 16th June 2021 |
| Notes | Healthy human iPSC clone with doxycycline-inducible expression of cytosolic Grx1-roGFP2 |
| User feedback | |
Provider |
|
| Generator | Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences (ICG) |
| Owner | Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences (ICG) |
| Derivation country | Russia |
External Databases |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA9218647 |
General Information |
|
| * Is the cell line readily obtainable for third parties? |
Yes Cell line can only be used in: Any
Research use: allowed
Clinical use: not allowed
Commercial use: not allowed
|
| Subclone of | |
Donor Information
General Donor Information |
|
| Sex | female |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian |
Phenotype and Disease related information (Donor) |
|
| Diseases | No disease was diagnosed.
|
Other Genotyping (Donor) |
|
| Is there genome-wide genotyping or functional data available? |
Yes
Exome sequencing
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/?term=SRR11413028 No disease associated mutation found |
External Databases (Donor) |
|
| BioSamples | SAMEA6983569 |
Ethics
Also have a look at the ethics information for the parental line
ICGi021-A
.
| For generation of the cell line, who was the supplier of any recombined DNA vectors or commercial kits used? |
hIPSC Derivation
General |
|
|
The source cell information can be found in the parental cell line
ICGi021-A.
|
|
Reprogramming method |
|
| Vector type | Non-integrating |
| Vector | Episomal |
| Is reprogramming vector detectable? |
No |
| Methods used |
PCR
|
| Files and images showing reprogramming vector expressed or silenced | |
Vector free reprogramming |
|
| Type of used vector free reprogramming factor(s) |
None
|
Other |
|
| Derived under xeno-free conditions |
No |
| Derived under GMP? |
No |
| Available as clinical grade? |
No |
Culture Conditions
| Surface coating | Gelatin | ||||||||||||||||||
| Feeder cells |
MEF cell Cellfinder Ont Id: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/efo/EFO |
||||||||||||||||||
| Passage method |
Enzymatically
TrypLE
|
||||||||||||||||||
| O2 Concentration | 20 % | ||||||||||||||||||
| CO2 Concentration | 5 % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Medium |
Other medium:
Base medium: Knock-out DMEM
Main protein source: Knock-out serum replacement Serum concentration: 15 % Supplements
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at passage previously with this cell line? | Yes |
||||||||||||||||||
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at cryo previously with this cell line? | No |
||||||||||||||||||
| Has Rock inhibitor (Y27632) been used at thaw previously with this cell line? | Yes |
Characterisation
Analysis of Undifferentiated Cells
| Marker | Expressed | Immunostaining | RT-PCR | Flow Cytometry | Enzymatic Assay | Expression Profiles |
| POU5F1 (OCT-4) |
Yes |
|||||
| SSEA-4 |
Yes |
|||||
| Alkaline Phosphatase |
Yes |
Morphology pictures
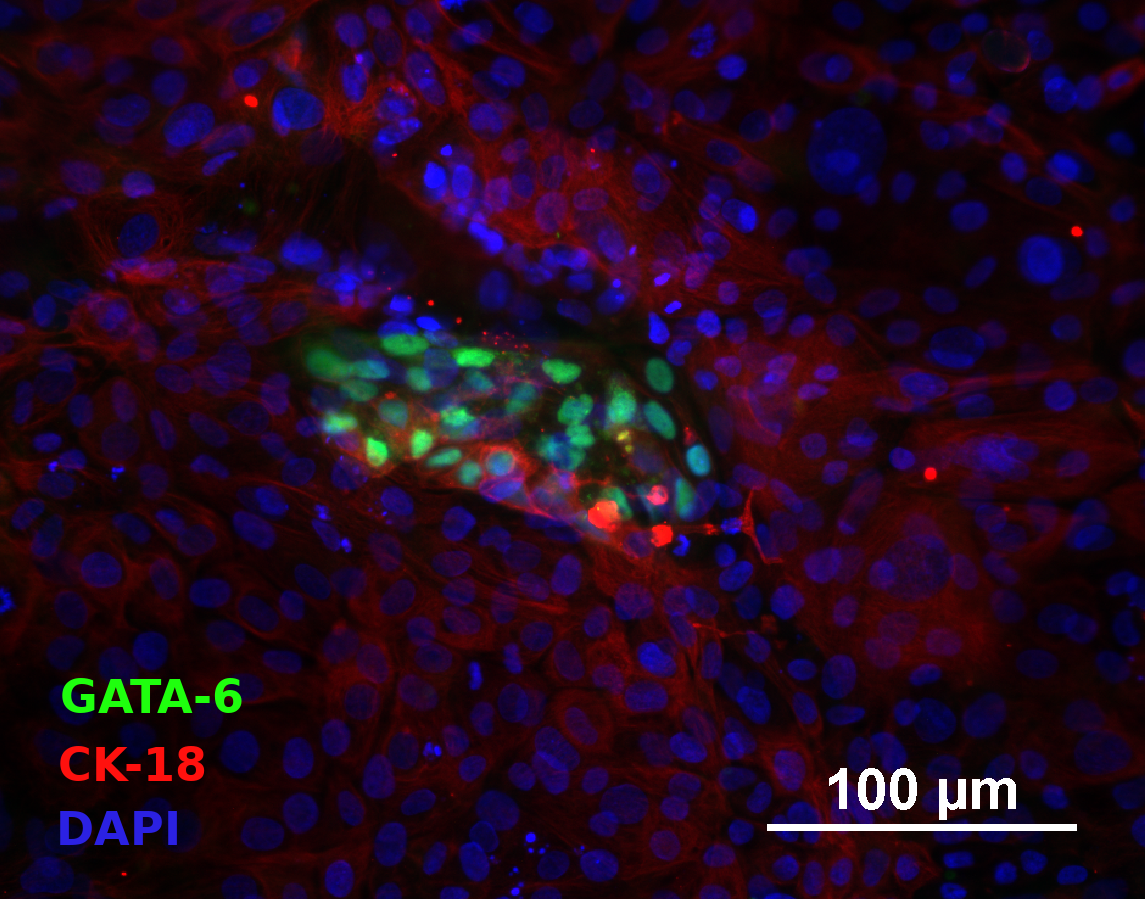
Differentiation Potency
In vitro spontaneous differentiation
In vitro spontaneous differentiation
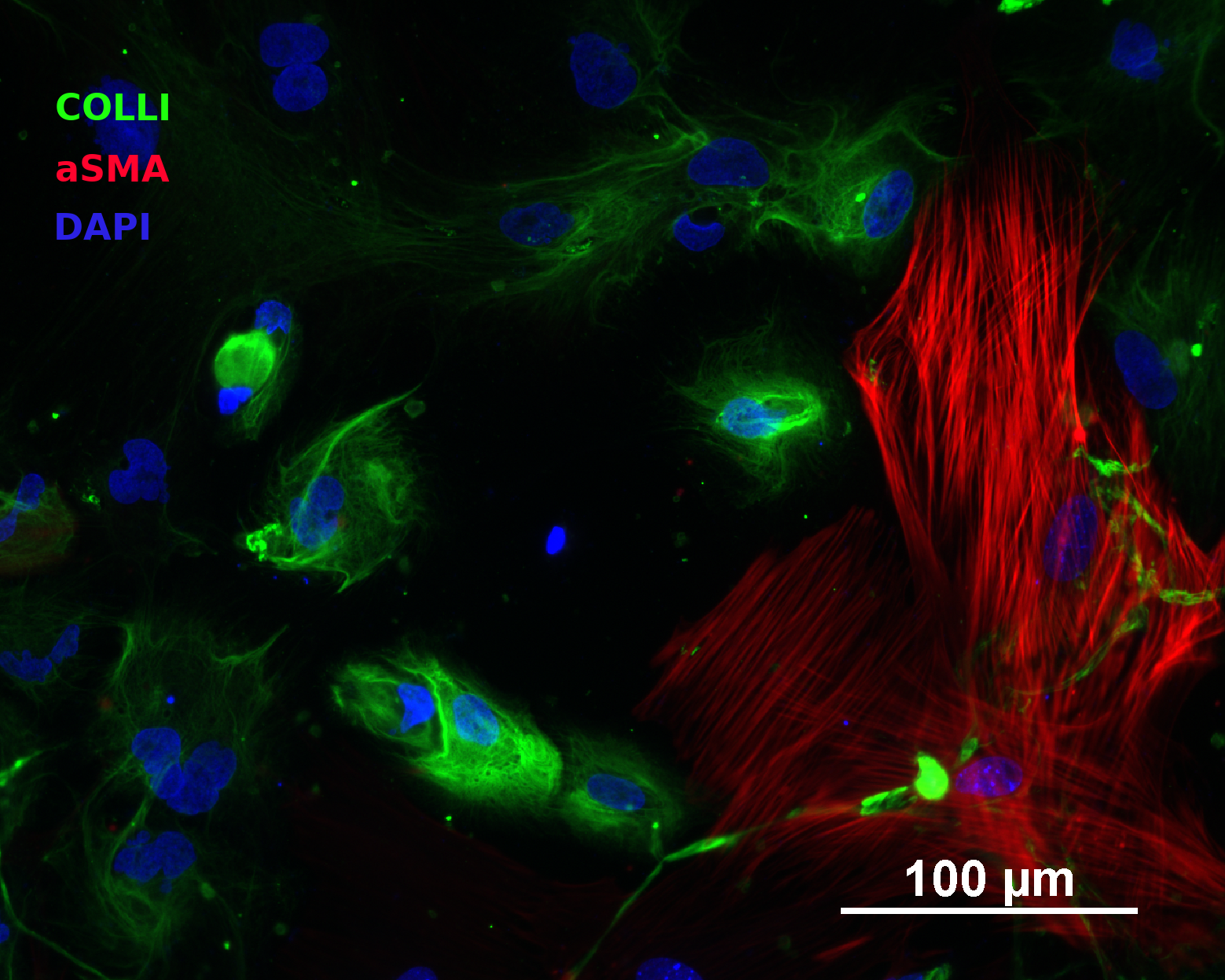
In vitro directed differentiation
| Marker | Expressed |
| Collagen type I |
Yes |
| aSMA |
Yes |
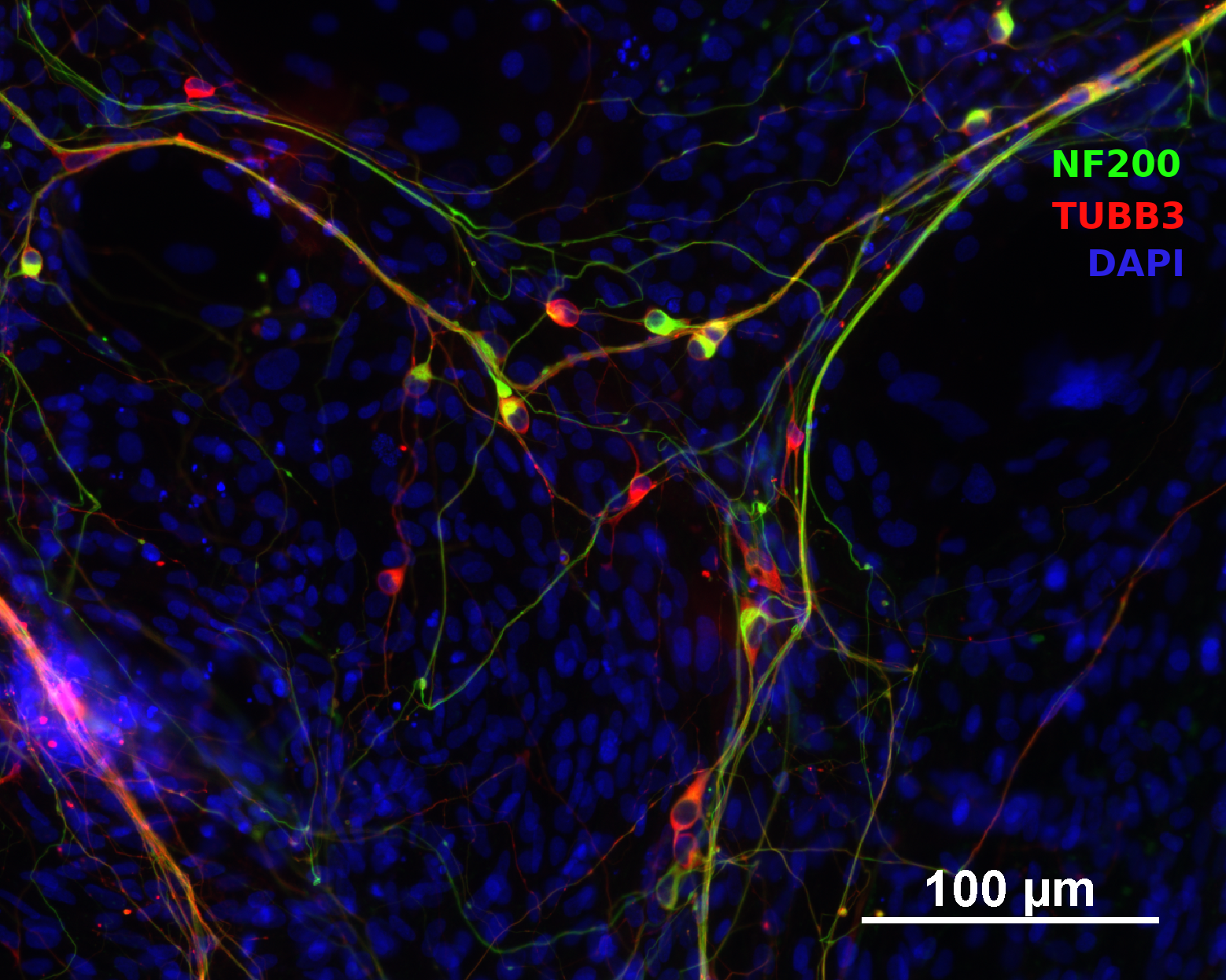
In vitro spontaneous differentiation
In vitro directed differentiation
| Marker | Expressed |
| Tubulin, beta 3 |
Yes |
| Neurofilament 200 |
Yes |
Microbiology / Virus Screening |
|
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
Genotyping
Karyotyping (Cell Line) |
|
| Has the cell line karyotype been analysed? |
Yes
|
Other Genotyping (Cell Line) |
|
Genetic Modification
| Disease/phenotype related modifications |
|
| Genetic modifications not related to a disease |
|


Login to share your feedback, experiences or results with the research community.